AFCTFA: A Potential Boost for African Economies
By Eslam Shaaban
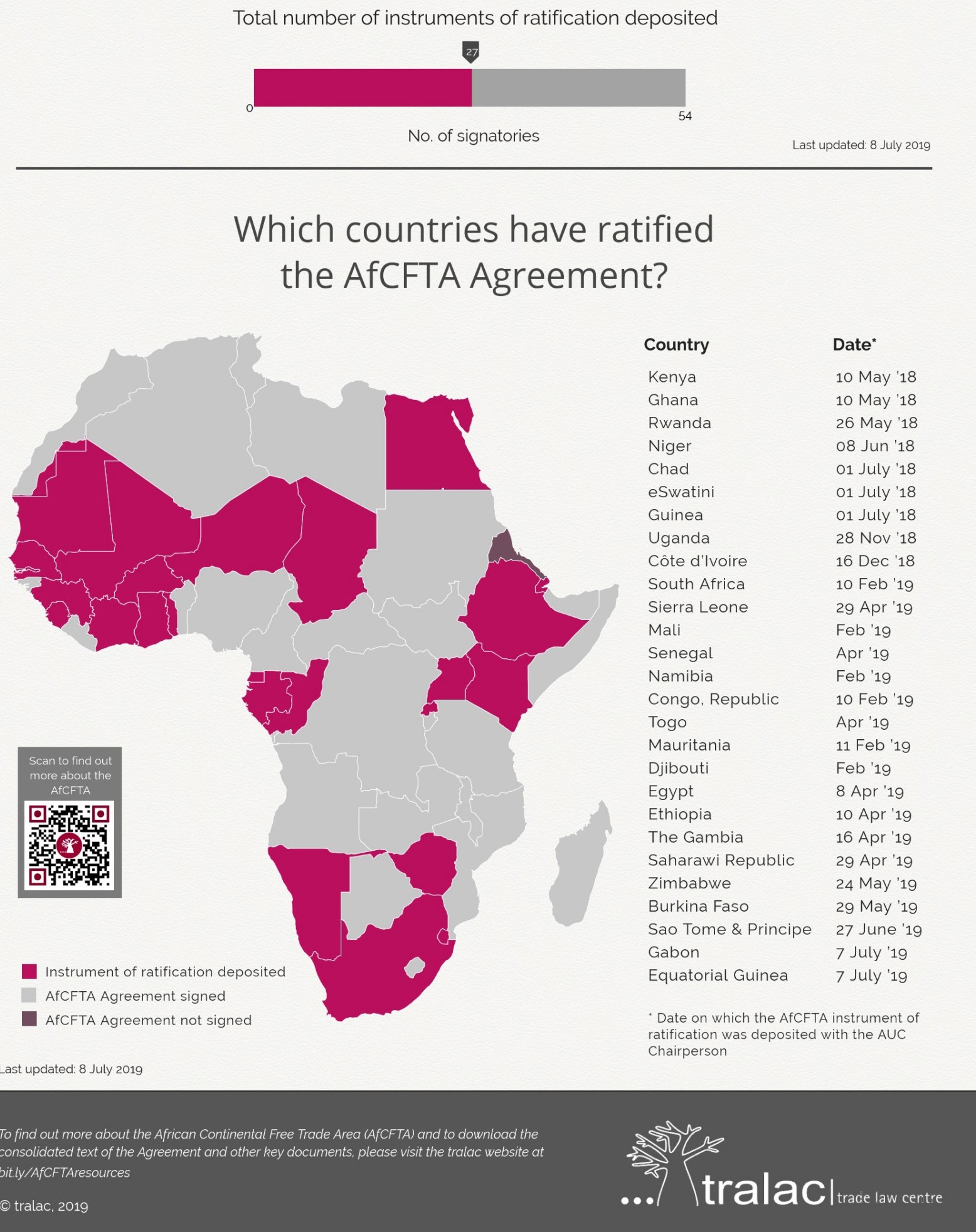
In March 2018, the African Continent Free Trade Agreement (AFCFTA) was unveiled as the world’s largest free trade area since the creation...
Community Biology Lab’s Response to COVID-19 in Africa: The Case of...
In order to successfully combat the Covid-19 pandemic, research must be accelerated in a collaborative and coordinated manner, by sharing knowledge and data in resource-constrained areas.
The Maker Movement Across North Africa (Arabic)
نغم الحسامي ونجلاء رزق
Authored by: Nagham El Houssamy and Dr. Nagla Rizk
نسعى من خلال ورقة العمل هذه لتوضيح مخرجات...
Open AIR Students Present at Carleton’s Institute of African Studies
Back in October 2016, three of our Open AIR Research Fellows had the unique and rewarding opportunity to participate in the Second Annual Institute of African Studies Undergraduate Research Conference at Carleton University’s Institute of African Studies. Undergraduate researchers from across the globe presented their research findings on a wide breadth of topics – from fiction describing Nigerian culture, to professional development for youth in South Africa, to political structures that influenced the welfare state in Tanzania and Kenya.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Learning in Ethiopia’s Textile and Garment...
Authored by : Bertha Vallejo and Tadesse Getachew Mekonnen
Abstract: Theoretically, foreign direct investment (FDI) favours industrial upgrading by allowing local firms to learn from...
Recognizing Africa’s innovation revolution: Leaders driving inclusive innovation receive Impact award
Solutions to some of society’s most important challenges require the right regulatory environment to drive innovation. Examples include pioneering models for access to educational...
Everywhere Still Invisible: Women and Their Traditional Knowledge
By Ghazaleh Jerban
I was so excited to be travelling to South Africa as an Open AIR NERG and QEScholar, in the middle of Canada’s notorious winter...
Gender, IP, and Innovation: Open AIR’s Future Research
The Open AIR network seeks to bring, among other things, a gendered perspective to our research. We are exploring the nexus between feminist literature, intellectual property, information technology, and innovation; connecting these approaches into the network’s future priorities.
Empowering Indigenous Craft Women in Africa
By Desmond Oriakhogba
As an Open AIR NERG and QEScholar, I have been conducting research since June 2018 on the empowerment of indigenous craft women...
COVID-19: My Experience, My Reflections
By Esther Adekunbi
My expectations and
enthusiasm to explore this beautiful land called Canada, to interact with its
friendly people, to network and collaborate, was rudely...